
Understanding the Reason of Hair Fall in Female: Causes and Solutions
Share
It can be really unsettling when you start noticing more hair in your brush or shower drain than usual. Many women experience hair fall at some point, and it's totally normal to wonder why. There are a bunch of different reasons this can happen, from everyday stuff to things that need a doctor's attention. Let's break down the common reasons for hair fall in female and what you can do about it.
Key Takeaways
- It's normal to lose about 50-100 hairs daily as part of the natural hair growth cycle.
- Common causes of hair fall in women include genetics (female pattern baldness), hormonal changes (like during menopause or PCOS), stress, and certain medications.
- Nutritional gaps, especially iron deficiency, and scalp conditions like infections can also lead to thinning hair.
- Noticeable thinning, hair falling in clumps, or bald patches are signs that warrant professional evaluation.
- Treatment options vary widely, from topical solutions and supplements to medical therapies, and a dermatologist can help find the best approach.
Understanding Normal Hair Shedding Versus Hair Loss
It's totally normal to find a few strands of hair here and there. We all shed hair every day, and it's usually not something to worry about. Think of it like leaves falling off a tree – it's just part of a natural process. But sometimes, what seems like normal shedding can actually be a sign of something more. Knowing the difference is key to keeping your hair healthy.
The Natural Hair Growth Cycle
Our hair doesn't just grow non-stop. It actually goes through different phases. Most of the hair on your head, about 85-90%, is in the 'anagen' or growing phase, which can last for years. Then there's a short 'catagen' phase, where growth slows down. After that, hair enters the 'telogen' or resting phase, which lasts a couple of months. Finally, in the 'exogen' phase, the hair sheds, and a new one starts to grow from the same follicle. This cycle means that losing some hair daily is completely expected.
Here's a quick look at the hair growth phases:
- Anagen (Growing Phase): The longest phase, where hair actively grows.
- Catagen (Transition Phase): A brief period where hair growth stops.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): Hair rests before shedding.
- Exogen (Shedding Phase): Hair detaches and falls out, making way for new growth.
Distinguishing Between Daily Shedding and Concern
So, how much hair loss is too much? Generally, losing between 50 to 100 hairs a day is considered normal. If you wash your hair daily, you might see a bit more, maybe up to 250 strands on that day. This is still within the normal range because of the shedding phase. However, if you start noticing significantly more hair than usual left in your brush, on your pillow, or in the shower drain, it might be time to pay closer attention. Consistent shedding of more than 100 hairs daily is often a sign that something else might be going on.
It's easy to get anxious about hair loss, but understanding the normal cycle helps put things in perspective. Most of the time, what you're seeing is just the natural turnover of hair. However, if the shedding seems excessive or you notice thinning, it's worth investigating further.
Some signs that suggest it's more than just normal shedding include:
- Noticeable thinning of hair, especially at the part line or crown.
- Hair falling out in large clumps after brushing or washing.
- Sudden or rapid hair loss.
- Bald patches appearing on the scalp.
- Scalp irritation, itching, or redness accompanying the hair loss.
If you're experiencing any of these, it's a good idea to consult a doctor to figure out the cause.
Common Reasons for Hair Fall in Females
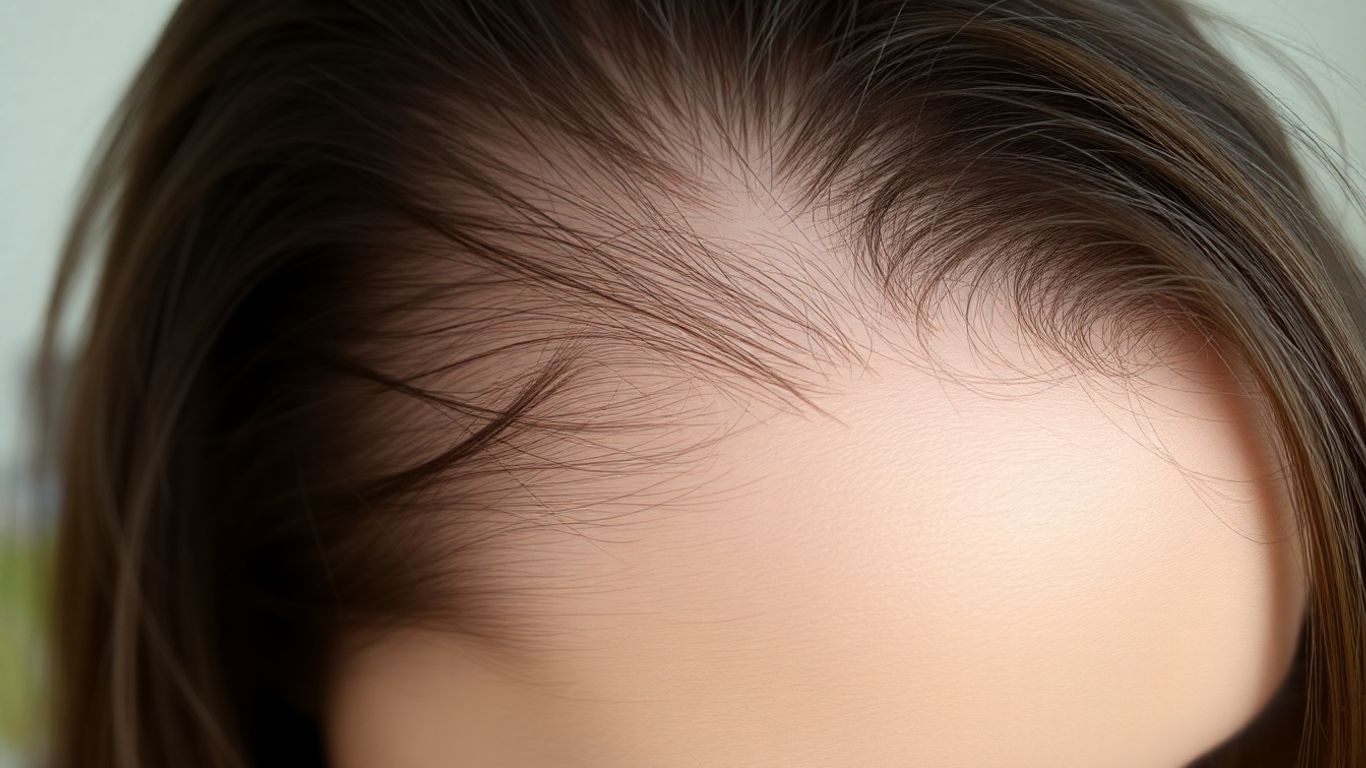
It's really common for women to experience hair loss, and it can be pretty upsetting. While men often get more attention for thinning hair, up to 40% of women might notice it by the time they're 50. But honestly, it can happen at any age. The way it looks can be different too; instead of a receding hairline, you might notice your hair part getting wider, or your ponytail feeling a lot less full than it used to. It's normal to shed some hair every day, usually between 50 and 100 strands. You might see more in the shower or on your brush, especially on wash days. But if you suddenly see way more hair falling out, or if you can see more scalp than before, it's worth looking into.
Genetics and Female Pattern Baldness
This is probably the most talked-about reason for hair loss in women, often called androgenetic alopecia. It's basically inherited, so it can come from either side of your family. It doesn't always show up super early, but it can start as early as your late teens, though many women notice it more in their 50s or 60s. What happens is your hair follicles gradually get smaller, and the hair growth cycle shortens. So, hairs shed, but the new ones that grow back are finer and thinner. Eventually, some follicles might stop producing hair altogether. You likely won't lose all your hair with this type, but without doing anything about it, it can get worse over time.
Hormonal Fluctuations and Imbalances
Hormones play a big role in how our hair grows and how thick it is. When hormone levels change a lot, it can mess with the hair cycle. Think about times like pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause. During menopause, for example, estrogen and progesterone levels drop, and this can lead to hair thinning. Thyroid issues can also throw your hormones out of whack and affect your hair.
Stress and Emotional Trauma
Ever heard of hair falling out after a really stressful period? That's a real thing, and it's often called telogen effluvium. It happens when a lot of hair follicles suddenly jump into the resting phase instead of continuing to grow. So, more hair falls out, and not enough new hair grows to replace it. This can be triggered by big life events, like a severe illness, a high fever, or even just a really tough emotional time. It's usually temporary, but sometimes it can stick around for a while.
Medications and Medical Treatments
Sometimes, the medicines we take for other health issues can have hair loss as a side effect. This includes things like certain antidepressants, blood thinners, birth control pills, and even treatments for arthritis. Of course, chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer are well-known for causing hair loss because they target fast-growing cells, including those in hair follicles. The good news is that hair often starts to grow back after you finish these treatments, though it might not be exactly the same as before.
It's important to remember that hair loss in women is complex and can have multiple contributing factors. What might cause thinning for one person could be entirely different for another. Identifying the specific reason is the first step toward finding a solution that works for you.
Here are some common triggers for telogen effluvium:
- Childbirth
- Severe infections or high fever
- Crash diets low in calories and protein
- Significant psychological stress, depression, or anxiety
- Thyroid disease
Nutritional Deficiencies Contributing to Hair Loss

Sometimes, the reason your hair is thinning or falling out isn't some big, scary disease, but simply that your body isn't getting enough of the good stuff it needs to keep your hair healthy. It's easy to overlook what we eat, but our hair follicles are pretty demanding when it comes to nutrients. When your diet is lacking, your hair often shows it first.
The Role of Iron in Hair Health
Iron is a big player in keeping your hair growing strong. It's what helps carry oxygen to your hair follicles. Without enough iron, those follicles can't get the oxygen they need, and this can lead to increased shedding. This is super common in women, especially those with heavy periods or who don't eat a lot of red meat. Low iron levels can really weaken the hair strands, making them more prone to breaking and falling out.
Impact of Vitamin Deficiencies
Several vitamins are also key for hair. For instance, B vitamins, particularly biotin (B7), are often talked about for hair health. But other B vitamins like B2, B3, B9, and B12 also play a role in cell turnover and nutrient delivery to the scalp. Vitamin D is another one that seems to be linked to hair follicle cycling. And don't forget Vitamin C, which helps your body absorb iron and is an antioxidant that protects follicles. Vitamin E is also an antioxidant that can help protect your scalp.
Other Essential Minerals for Hair Growth
Beyond iron and vitamins, other minerals are important too. Zinc is vital for hair tissue growth and repair. It also helps keep the oil glands around the follicles working properly. Selenium is another mineral that plays a role in hair production. If you're not getting enough of these, your hair might become brittle and fall out more easily. It's a delicate balance, and sometimes just a few small changes can make a difference. If you're worried about your nutrient intake, talking to a doctor about a blood test might be a good idea to check for any specific deficiencies. You can find more information on how nutrition impacts hair health here.
It's not just about eating enough food, but eating the right kinds of food. A diet that's too restrictive, or one that's heavy on processed items and light on whole foods, can leave your body, and your hair, wanting.
Here's a quick look at some common culprits:
- Iron: Crucial for oxygen transport to follicles. Deficiency is a frequent cause of hair loss in women.
- Zinc: Important for hair growth and repair, and scalp oil gland function.
- B Vitamins (especially Biotin): Involved in cell growth and nutrient delivery.
- Vitamin D: Linked to hair follicle cycling.
- Vitamin C: Aids iron absorption and protects follicles.
- Vitamin E: Another antioxidant for scalp health.
- Protein: Hair is made of protein, so adequate intake is necessary.
Scalp Conditions and Their Effect on Hair
Sometimes, the reason your hair is falling out isn't just about what's happening inside your body or your genes. The health of your scalp plays a pretty big role too. Think of your scalp as the soil for your hair; if the soil isn't healthy, the plants (your hair) won't thrive.
Infections Leading to Follicle Damage
Scalp infections can really mess with your hair growth. One common culprit is ringworm of the scalp, or tinea capitis. It's a fungal infection that can cause those annoying patchy bald spots we talked about. It doesn't just sit on the surface; it can actually damage the hair follicles, making it hard for hair to grow back in those areas. Another issue is folliculitis, which is inflammation of the hair follicles, often caused by bacteria. This can lead to little red bumps and, you guessed it, hair loss around those inflamed spots.
Inflammatory Scalp Issues
Beyond outright infections, general inflammation on the scalp can also be a problem. Conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, which causes dandruff, redness, and itching, can create an unhealthy environment for hair growth. When your scalp is constantly irritated and inflamed, it can weaken the hair and contribute to shedding. It's like trying to grow a garden during a constant dust storm – not ideal for healthy roots.
It's easy to overlook scalp health when we're focused on hair loss, but a healthy scalp is the foundation for healthy hair. Addressing any underlying infections or inflammatory conditions is a key step in getting your hair back on track.
Here are some signs that a scalp condition might be contributing to your hair fall:
- Persistent itching or burning sensations on your scalp.
- Visible redness, scaling, or flaky patches that don't go away with regular shampooing.
- Soreness or tenderness when you touch your scalp.
- Noticeable thinning of hair in specific areas, especially if accompanied by scalp irritation.
Recognizing When Hair Loss Requires Professional Attention
Signs of Significant Hair Loss
It's normal to shed some hair every day, usually between 50 to 100 strands. This is just part of the hair's natural growth cycle. But sometimes, what seems like normal shedding can actually be a sign that something more is going on. If you're noticing a lot more hair than usual on your brush, in the shower drain, or on your pillow, it might be time to pay closer attention. Sudden or excessive hair fall, especially if it's happening quickly, is a key indicator that you should seek professional advice.
Here are some things to watch out for:
- Consistently shedding more than 100 hairs daily.
- Visible thinning, particularly at the crown or widening of your hair part.
- Hair coming out in noticeable clumps after washing or brushing.
- Developing bald spots, even small ones, on your scalp.
- Experiencing itching, redness, or scaling on your scalp along with hair loss.
Sometimes, hair loss can be a symptom of an underlying health issue. It's easy to brush it off, but ignoring persistent changes could mean missing a chance to address a problem early on. Think of it like a check engine light in your car – it's telling you something needs a look.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
While a little extra shedding might not be a big deal, there are definitely times when you should make an appointment with a dermatologist or a hair specialist. Don't wait too long, as early intervention can sometimes prevent permanent damage to your hair follicles. You should consider seeing a doctor if:
- You've tried over-the-counter remedies for a few months without seeing any improvement.
- Your hair loss is sudden and severe, or you notice patchy bald spots.
- You're experiencing other symptoms that might be related, like changes in your menstrual cycle, fatigue, or skin issues.
- You have a family history of hair loss, like female pattern baldness.
- The hair loss is causing you significant distress or affecting your self-esteem.
Diagnostic Approaches for Hair Loss
When you see a doctor about hair loss, they'll want to get a clear picture of what's happening. They'll likely start by asking you a bunch of questions about your health history, when you first noticed the hair loss, and if anyone in your family experiences similar issues. They'll also do a physical exam, looking closely at your scalp and hair. Sometimes, they might do a "hair pull test" to see how easily hairs come out. Depending on what they suspect, they might also order blood tests to check for things like thyroid problems, vitamin deficiencies, or other health conditions that could be contributing to your hair loss.
Effective Treatment Options for Female Hair Loss
Okay, so you've figured out why your hair might be thinning, and now you're wondering what can actually be done about it. The good news is, there are quite a few ways to tackle female hair loss, and what works best really depends on what's causing it in the first place. It's not a one-size-fits-all situation, so talking to a doctor is usually the first smart move.
Topical Solutions and Medications
When it comes to treatments you can apply yourself, minoxidil is probably the most well-known. You can get it over the counter in different strengths, usually as a liquid or foam that you apply directly to your scalp. It works by making your hair follicles stay in the growing phase longer, giving your hair more time to grow out. It's important to remember that consistency is key with minoxidil; you often need to use it for several months before you see any real changes, and you typically have to keep using it to maintain the results.
Sometimes, doctors might prescribe other medications, especially if there's a hormonal component to your hair loss. Drugs like spironolactone can help by blocking certain hormones that might be contributing to thinning. These are usually taken orally and require a prescription.
Hormonal Therapies and Supplements
If your hair loss is linked to hormonal shifts, like those during menopause or due to conditions like PCOS, hormonal therapies might be an option. This could involve certain birth control pills or other hormone-regulating treatments. It's all about trying to rebalance things in your body.
Supplements are another area people explore. If blood tests show you're low in things like iron, vitamin D, or biotin, your doctor might suggest specific supplements. It's really not a good idea to just start popping pills, though. Taking too much of certain vitamins or minerals can actually be harmful, and they can sometimes mess with other medications you might be taking. Always get a doctor's advice on this.
Here's a quick look at some common supplements and their roles:
- Iron: Absolutely vital for carrying oxygen to your hair follicles. Low iron is a super common reason for hair loss in women.
- Vitamin D: Plays a part in creating new follicles. Many people are deficient without even knowing it.
- Biotin (Vitamin B7): Often linked to hair health, though evidence for its effectiveness in non-deficient people is mixed.
- Zinc: Important for hair tissue growth and repair.
Advanced Treatments and Procedures
For those looking for more hands-on solutions, there are a few procedures that have gained traction. Low-level laser therapy, often delivered through devices like combs or caps, is FDA-approved for certain types of hair loss. The idea is that the light energy stimulates the hair follicles.
Microneedling is another technique. It involves using tiny needles to create small punctures in the scalp, which can help stimulate hair growth, especially when combined with topical treatments like minoxidil. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is also an option. This involves drawing your blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting that plasma back into your scalp. The growth factors in the platelets are thought to encourage hair regrowth.
When considering any treatment, especially prescription medications or procedures, it's really important to have an open chat with your doctor. They can help you understand the potential benefits, side effects, and whether a particular treatment is safe for you, especially if you're pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. What works for one person might not be the best fit for another, and a professional can guide you toward the most suitable path for your specific situation.
Hair transplant surgery is also an option, though it's usually considered for more significant hair loss. This involves taking hair from a fuller area of your scalp and transplanting it to thinning areas. It's a more involved procedure, but it can offer permanent results.
Wrapping It Up: You've Got This
So, we've talked a lot about why hair might be falling out and what you can do about it. It can feel pretty overwhelming, right? But the main takeaway here is that you're definitely not alone in this. Lots of women deal with hair thinning or loss for all sorts of reasons, from stress to just getting older. The good news is, there are ways to figure out what's going on and find solutions that work for you. Don't hesitate to chat with a doctor or a dermatologist if you're worried. They can help pinpoint the cause and guide you toward the best treatment. Taking that first step is often the hardest part, but it's totally worth it for your hair and your peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much hair loss is normal for women?
It's totally normal to lose about 50 to 100 hairs each day. This happens because your hair has a natural growth cycle, and some hairs are always in the 'resting' or 'shedding' phase. Think of it like leaves falling off a tree in autumn – it's just part of the process!
What's the most common reason women lose hair?
The most common cause is something called 'female pattern baldness,' also known as androgenetic alopecia. It's often passed down in families and can cause hair to get thinner over time, especially on the top of the head. Hormones can also play a big role, especially around menopause.
Can stress really make my hair fall out?
Yes, it absolutely can! Big stressful events, like surgery, childbirth, or even a very emotional time, can shock your hair follicles. This can cause a lot of hair to enter the resting phase all at once, leading to more shedding a few months later. This is often called telogen effluvium.
Are there vitamins or minerals that help with hair loss?
Definitely! Your hair needs good nutrition to grow strong. Iron is super important because it helps carry oxygen to your hair roots. Not getting enough iron, or certain vitamins like B vitamins, vitamin D, and zinc, can lead to weaker hair and more shedding.
When should I see a doctor about my hair loss?
If you're losing more than 100 hairs daily for a while, notice bald spots, or your hair is thinning a lot, it's a good idea to see a doctor, especially a dermatologist. Also, if you have other symptoms like scalp itching or redness, or if the hair loss started suddenly, get it checked out.
What are some ways to treat hair loss in women?
There are several options! Doctors might suggest special lotions or medicines you put on your scalp, like minoxidil. Sometimes, taking supplements for vitamin deficiencies helps. For more serious cases, there are treatments like light therapy, injections, or even hair transplant surgery. The best treatment depends on why you're losing hair.
