Decoding the Different Types of Hair Baldness: A Comprehensive Guide
Share
Hair loss is something a lot of people deal with, and it shows up in different ways. It’s not just about how you look; it can really affect how you feel about yourself. Knowing the different types of baldness is the first step to figuring out what might be causing it and what you can do about it. This guide breaks down the common types of hair loss so you can get a better idea of what's going on.
Key Takeaways
- Androgenetic alopecia, often called male or female pattern baldness, is the most common reason for hair loss.
- The Norwood Scale is a way to measure how male pattern baldness progresses, with seven stages showing different levels of hair loss.
- Traction alopecia happens from hairstyles that pull too much on your hair, like tight braids or ponytails.
- Figuring out which type of hair loss you have is important for finding the right treatment.
- Treatments can include medicines like minoxidil and finasteride, hair transplant surgery, and making changes to your lifestyle and hair care routine.
Understanding the Different Types of Hair Baldness
Hair loss is something a lot of people deal with, and it shows up in different ways. It's not just about how you look; it can really affect how you feel about yourself. Figuring out what kind of hair loss you have is the first step to finding what works best for you.
Androgenetic Alopecia: The Most Common Culprit
This is the big one, the most common reason people lose hair. You might know it as male pattern baldness or female pattern baldness. For guys, it usually starts with a hairline that moves back, and then thinning happens at the top, often ending in that classic horseshoe shape. Women usually see their part get wider, and the thinning is more spread out all over the scalp, but the front hairline usually stays put. It's largely tied to genetics and hormones.
Male Pattern Baldness Explained
Male pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is pretty much the standard for hair loss in men. It's hereditary, meaning it runs in families, and male hormones play a big role. You'll often see it start with a receding hairline, making an 'M' shape, and then thinning at the crown. It's a gradual process, and the pattern is quite predictable.
Female Pattern Baldness Characteristics
When women experience androgenetic alopecia, it's a bit different. Instead of a receding hairline, they typically notice their hair becoming thinner all over, especially on the top of their head. The part line often widens, and while there's thinning, the frontal hairline usually remains intact. It's less about a distinct pattern and more about a general reduction in hair volume.
Exploring the Norwood Scale for Male Pattern Baldness
When we talk about male pattern baldness, you'll often hear about the Norwood Scale. It's basically a way doctors and hair specialists use to measure how much hair loss a guy is experiencing and what pattern it's following. Think of it like a map for hair loss, showing the different stages from barely noticeable thinning to more significant baldness. It was first put together by Dr. James Hamilton back in the 1950s and later updated by Dr. O’Tar Norwood, which is why it has his name. This scale helps everyone involved get on the same page about the situation and figure out the best way to approach treatment.
Deciphering the Norwood Scale: A Comprehensive Guide
The Norwood Scale is a system that classifies the progression of male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia. It's broken down into seven distinct stages, each representing a different level of hair loss and a specific pattern. The scale primarily focuses on the receding hairline at the temples and the thinning or loss of hair on the crown (vertex). It's a visual tool that helps doctors assess the severity of hair loss and discuss potential treatments with patients. While it's a widely accepted standard, it's important to remember it mainly tracks the extent of baldness, not necessarily hair density within the affected areas.
Unveiling the Seven Stages of Hair Loss Progression
The Norwood Scale outlines seven stages of male pattern baldness:
- Stage I: No significant hair loss, or very minimal recession at the hairline.
- Stage II: Early signs of hair loss, with a slight recession of the hairline at the temples, forming a mature hairline.
- Stage III: The first stage where significant hair loss is noticeable. This typically involves more pronounced recession at the temples and possibly thinning on the crown.
- Stage IV: Hair loss progresses, with widening bald spots at the temples and a larger bald patch on the crown. These areas may start to connect.
- Stage V: The bald areas at the temples and crown become more distinct and larger, often separated by a narrow strip of hair.
- Stage VI: The receding hairline and bald crown merge, leaving a wider bald area across the top of the scalp. Only a band of hair remains on the sides and back.
- Stage VII: This is the most advanced stage, with hair loss extending to the sides and back of the head, leaving only a narrow horseshoe-shaped pattern of hair.
Understanding your specific stage on the Norwood scale is a key step in addressing hair loss. It provides a clear picture of the progression and helps in setting realistic expectations for treatment outcomes.
Practical Application of the Norwood Scale
So, how is this scale actually used? Well, doctors and hair restoration specialists use it to get a clear picture of your hair loss. They'll look at your scalp and compare it to the diagrams on the Norwood scale to determine which stage you're currently in. This assessment is pretty important because it helps them:
- Diagnose the type of hair loss: Confirming it's indeed male pattern baldness.
- Plan treatments: Different stages might respond better to certain treatments, like medications or hair transplant surgery options.
- Track progress: It allows for monitoring how effective treatments are over time.
- Discuss prognosis: Giving you an idea of what to expect in the future.
It's a really useful tool for getting a handle on what's happening with your hair and making informed decisions about what to do next. Knowing your Norwood stage is the first step in managing male pattern baldness effectively.
Other Significant Types of Hair Baldness
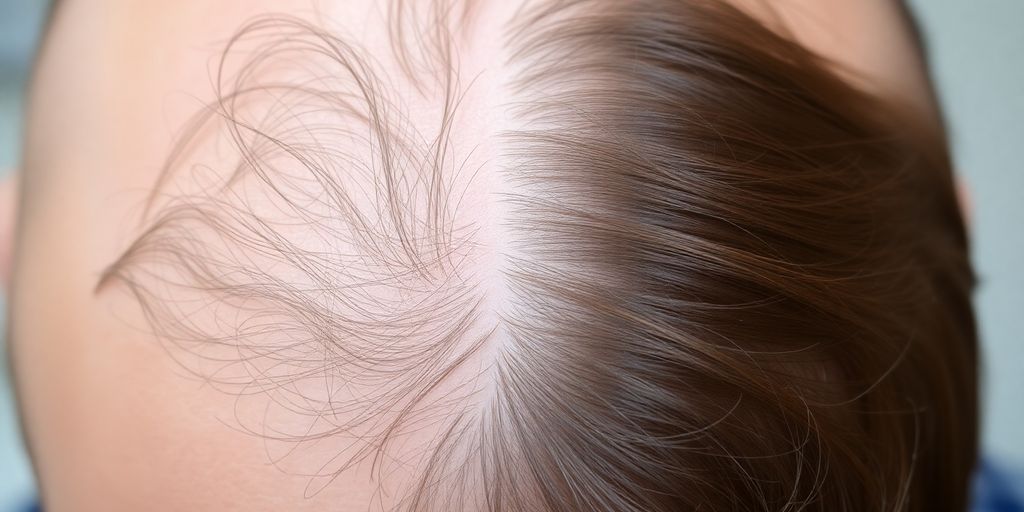
Traction Alopecia: Caused by Styling Habits
Traction alopecia is a type of hair loss that happens when your hair is pulled tightly for a long time. Think about hairstyles like tight braids, weaves, extensions, or even tight ponytails. When hair is constantly tugged, it can damage the hair follicles, leading to thinning or even permanent baldness in the affected areas. It often shows up along the hairline where the tension is greatest. The key to preventing traction alopecia is to be mindful of how you style your hair and avoid styles that pull too hard.
Identifying Your Specific Type of Hair Loss
Figuring out what kind of hair loss you're dealing with is the first step to getting it sorted. It's not always straightforward, as some types can look similar. For instance, androgenetic alopecia, the common pattern baldness, is often genetic. Then there's alopecia areata, which is an autoimmune issue where your body attacks its own hair follicles, causing patchy loss. Telogen effluvium is usually a temporary thing, often triggered by stress or a big life event, leading to more general thinning. Involutional alopecia is just a natural thinning that happens as we get older. Knowing the difference helps you and your doctor find the right treatment. It's a good idea to talk to a doctor or a dermatologist to get a proper diagnosis. They can help you understand if your hair loss is related to genetics, stress, styling, or something else entirely. Getting the right diagnosis is the first step toward finding effective hair restoration solutions.
Addressing Hair Loss: Treatment and Management

Dealing with hair loss can feel overwhelming, but the good news is there are many ways to manage it and even regrow hair. It's not just about accepting it; there are actual steps you can take. We'll look at the main treatments available, from pills and potions to more involved procedures, and also touch on how your daily habits can make a difference.
Medications for Hair Loss
When it comes to medical treatments, a couple of names pop up frequently. Minoxidil, often sold under brand names like Rogaine, is a topical solution you apply directly to your scalp. It's thought to work by widening blood vessels, which might help hair follicles grow. Then there's finasteride, a prescription pill (like Propecia) that works differently. It targets hormones, specifically DHT, which is a major player in male pattern baldness. By blocking DHT, it can slow down hair loss and, for some, even lead to regrowth. It's important to talk to a doctor before starting either of these, as they have specific ways they work and potential side effects.
Hair Transplant Surgery Options
For those looking for a more permanent solution, hair transplant surgery is a big step. The basic idea is moving hair from areas where it grows well to areas that are thinning or bald. Two common methods are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT involves taking a strip of skin with hair from the back of your head and then dividing it into tiny grafts. FUE, on the other hand, takes individual hair follicles directly from the scalp. Both aim to create a natural-looking result, but they have different recovery times and scarring patterns. It’s a significant procedure, so choosing a skilled surgeon is really key.
Lifestyle Choices for Hair Health
Beyond medications and surgery, what you do every day matters too. Eating a balanced diet is pretty important; think plenty of protein, vitamins like biotin and D, and minerals like iron. These are the building blocks for healthy hair. Regular exercise is also good because it boosts blood flow, including to your scalp, which can help hair follicles. On the flip side, try to cut back on smoking and excessive drinking, as these can negatively impact your overall health, including your hair. Even how you style your hair can play a role – tight hairstyles can cause stress on the follicles over time, leading to a type of hair loss called traction alopecia. So, maybe ease up on the super-tight ponytails or braids now and then.
Taking care of your hair often involves a combination of approaches. What works for one person might not work for another, so it’s about finding the right mix for your specific situation and being patient with the process. Consulting with a specialist can help you figure out the best path forward.
It's also worth considering things like scalp micropigmentation, which is a cosmetic procedure that can give the appearance of fuller hair by tattooing tiny dots onto the scalp. Some people also find low-level laser therapy helpful for stimulating hair growth. Remember, managing hair loss is a journey, and staying informed about the latest advancements in hair restoration can be beneficial.
Wrapping Up Our Hair Loss Journey
So, we've gone over a bunch of different reasons why hair might start thinning or falling out. From the common pattern baldness that many guys and gals deal with, to hair loss from tight hairstyles or even medical issues, it’s clear there’s a lot going on. Knowing which type you're facing is the first big step. It helps you figure out what treatments might actually work, whether that’s medication, a transplant, or just changing up how you style your hair. Don't hesitate to chat with a doctor or a hair specialist; they can really help pinpoint the cause and guide you toward the best plan for your situation. It’s a journey, for sure, but understanding is half the battle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is hair loss?
Hair loss is when you start losing more hair than usual. It can happen in different ways, like your hairline moving back or your hair getting thinner on top. It's pretty common and can be caused by things like genes, hormones, or how you style your hair.
What is the most common type of hair loss?
The most common kind is called androgenetic alopecia, which is just a fancy name for male or female pattern baldness. It's often passed down in families and has to do with certain hormones.
What is the Norwood Scale?
The Norwood Scale is like a map that helps doctors see how far male pattern baldness has progressed. It has seven stages, showing how the hairline moves back and the hair thins out over time.
Can hair loss be treated or reversed?
Yes, some hair loss can be fixed! If it's caused by tight hairstyles, changing your hair routine can help. For other types, like pattern baldness, there are medicines and even hair transplant surgeries that can help regrow hair.
How do I find out what type of hair loss I have?
It's a good idea to see a doctor or a hair specialist. They can look at your hair and scalp, ask about your health, and figure out exactly what's causing your hair loss. This helps them suggest the best treatment for you.
Are there things I can do in my daily life to help my hair?
Eating healthy foods, managing stress, and being gentle with your hair can all help keep it healthy. Avoiding super tight hairstyles is also important to prevent certain kinds of hair loss.
